Unearthing the Origins of Carnival: Evidence of Ancient Summer Festivals in Pre-Colonial Brazil
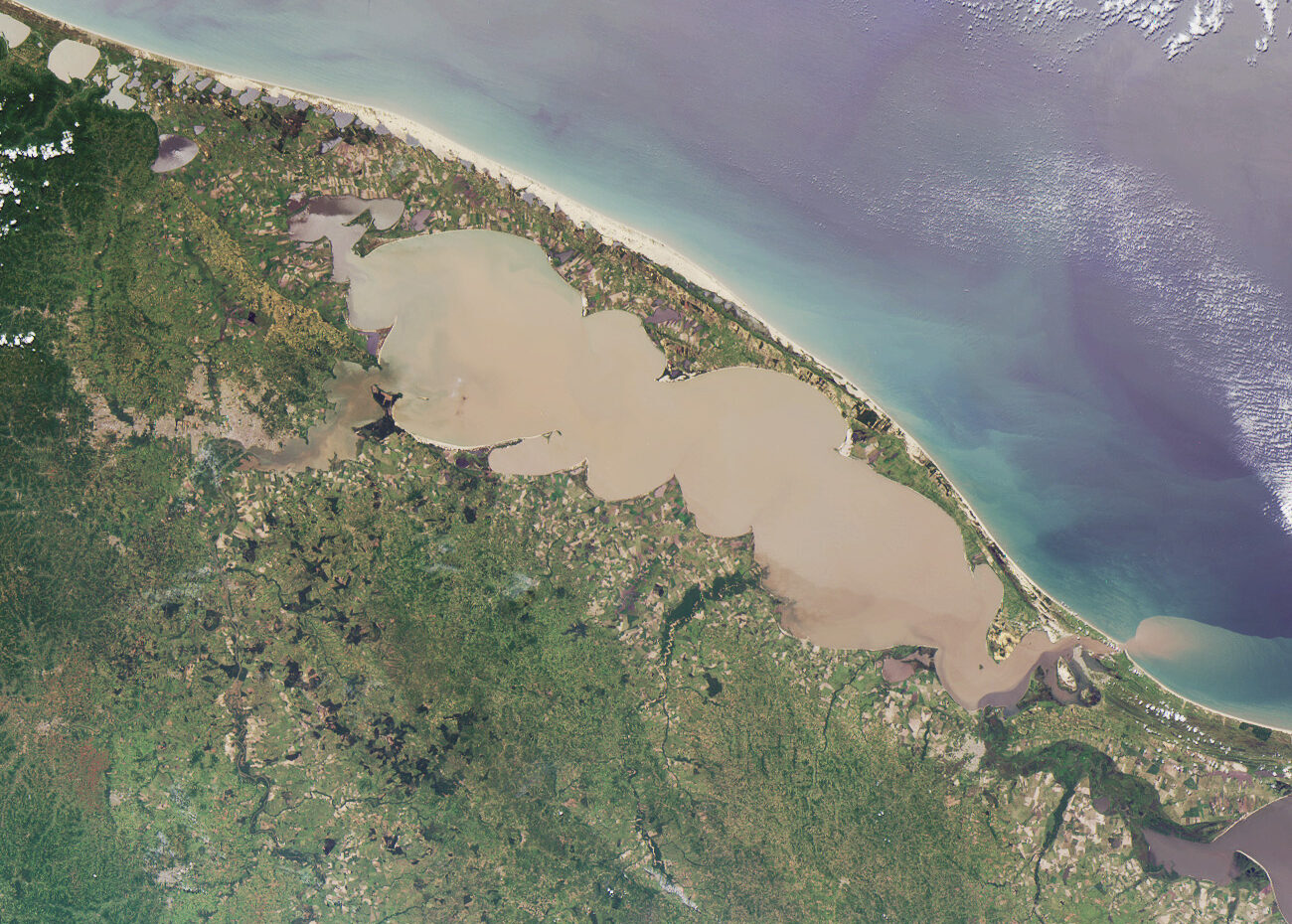

A new study suggests that pre-colonial people in Brazil gathered during the summer months to feast on migratory fish and share alcoholic drinks. An international team of scientists analyzed pottery fragments dating back between 2300 and 1200 years, discovered around the Patos Lagoon in Brazil.
The shores of the lagoon are characterized by settled earthen mounds known as “Cerritos,” built by the pre-colonial ancestors of Pampean Indigenous groups, including the Charrua and Minuano. The researchers identified some of the earliest evidence of alcoholic drink production in the region, with advanced analysis revealing traces of beverages likely made from tubers, sweet corn, and palm. Other pottery fragments contained evidence of fish processing.
This discovery strengthens the belief that pre-colonial people may have gathered around these mounds, which held symbolic significance as burial sites, territorial markers, and monuments, to celebrate and feast on seasonally abundant fish. Previous isotope analysis of ancient human remains from the area indicated that the inhabitants had diverse diets, suggesting that people may have traveled to the lagoon from a wider region.
Dr. Marjolein Admiraal, the lead author of the study, emphasized that seasonal gatherings at the mounds were important cultural events, bringing together dispersed communities to exploit and celebrate the return of migratory fish, such as the Whitemouth croaker, which likely required collective effort to process. “We see examples of such practices around the world, often related to the seasonal abundance of migratory species. These events provide excellent opportunities for social activities, such as funerals and marriages, and hold great cultural significance,” she stated.
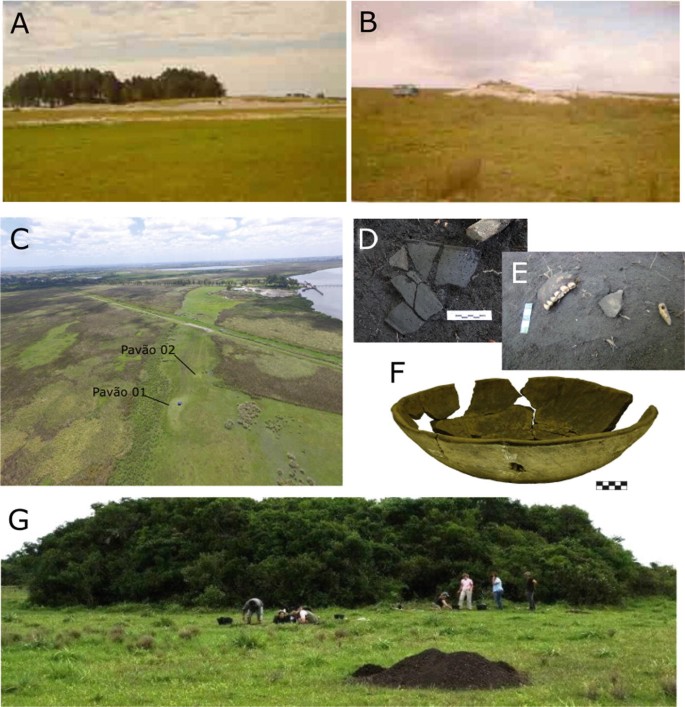
Archaeology of Fishing of the Earthen and Shell Moundbuilders (Cerritos and Sambaquis) of the Patos Lagoon, Southern Brazil, 3200–200 Years BP. Credit: Rafael Guedes Milheira, Flávio Rizzi Calippo & Manuel Haimovici
Archaeology of Fishing of the Earthen and Shell Moundbuilders (Cerritos and Sambaquis) of the Patos Lagoon, Southern Brazil, 3200–200 Years BP. Credit:Rafael Guedes Milheira, Flávio Rizzi Calippo & Manuel Haimovici
More:
https://arkeonews.net/unearthing-the-origins-of-carnival-evidence-of-ancient-summer-festivals-in-pre-colonial-brazil/

